J&K’s Hydropower Riches: Why is the Region Still Spending Billions on Power Purchases?
Jammu and Kashmir’s over-reliance on external power sources has incurred a substantial cost of Rs 63,000 crore over the past 11 years. This hefty expenditure on power purchases from external generation companies (gencos) underlines the ongoing energy challenge in the region, despite its substantial hydropower potential.
Official data reveals that from the fiscal year 2012-13 to 2022-23, the power purchase bills from external power distribution companies (discoms) have reached a cumulative total of Rs 63,000 crore.
In the most recent financial year, 2022-23, the Jammu and Kashmir government spent over Rs 8200 crore on purchasing electricity from external sources. This expenditure pattern remained consistent over the years, indicating a growing reliance on external power.
The persistent power crisis in the region is mainly attributed to a significant gap between the revenue generated by the Power Development Department (PDD) and the funds required for power purchases. The high Aggregate Transmission and Commercial (AT&C) losses, standing at a staggering 55 percent, are a significant part of the government’s liabilities. To prevent power disruptions, the government pays for power purchases in advance according to the Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with various generation companies, including central and J&K Gencos.
The government’s liability of Rs 31,000 crore, largely associated with these losses, underscores the magnitude of the energy challenge. This situation forces the region to buy power at higher rates in case of a shortage, adding to the financial burden.
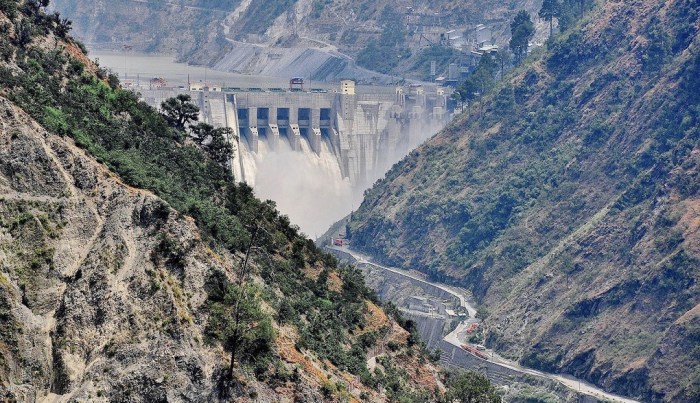
The Jammu and Kashmir government has now set ambitious targets to increase hydropower generation capacity substantially over the next few years. This includes the execution of 5 mega hydropower projects in collaboration with the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) that aims to add a total capacity of 4134 MW. These projects are expected to make J&K power surplus upon completion and are a part of the ongoing efforts to reduce the region’s dependence on external power sources.
The data highlights the urgency of improving the region’s energy infrastructure and achieving energy self-sufficiency to reduce the high costs associated with external power procurement. This move is not only crucial for ensuring a stable and affordable power supply but also for the overall development and sustainability of Jammu and Kashmir.