Cancer is a group of diseases that involve uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells anywhere in the body. Cancer cells are different from normal cells in many ways. For instance, cancer cells can multiply uncontrollably and form tumors, and they can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms of cancer: The symptoms of cancer can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. However, some common symptoms of cancer include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Pain
- Changes in appetite
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- A lump in the breast or other part of the body
- Changes in the skin, such as a mole that changes shape or size
- A persistent cough or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Headache
- Seizures
- Vision changes
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
Causes of cancer: Cancer is caused by changes in the DNA of a cell. DNA is the genetic material that contains the instructions for how to build and maintain a cell. When DNA is damaged, it can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer. There are many factors that can damage DNA, including:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Exposure to radiation, such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or X-rays
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as asbestos and benzene
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Hepatitis B and C infections
- Obesity
- A family history of cancer
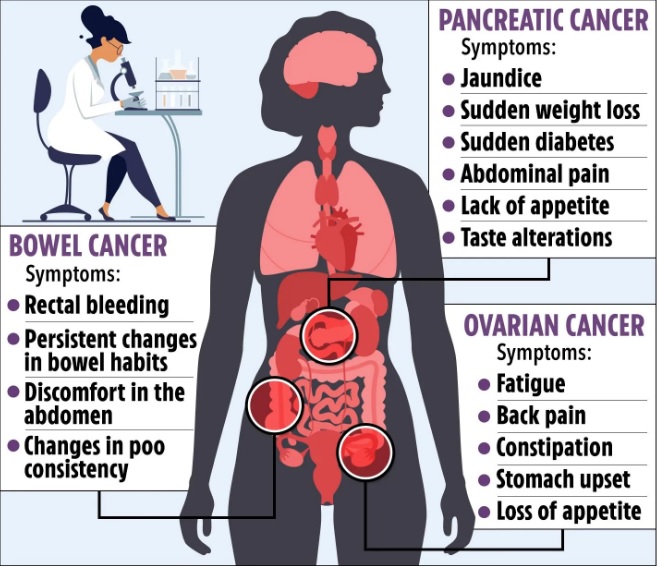
The three most undetectable cancers are:
- Pancreatic cancer: Pancreatic cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the pancreas, a gland that produces digestive enzymes and hormones. It is often difficult to detect because it does not usually cause symptoms until it is advanced.
- Ovarian cancer: Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the ovaries. It is often difficult to detect because it does not usually cause symptoms until it is advanced.
- Brain cancer: Brain cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the brain or spinal cord. It can be difficult to detect because the symptoms can vary depending on the location of the tumor.
While these cancers can be difficult to detect, there are some things that people can do to increase their chances of early detection.
- Pancreatic cancer: There is no screening test for pancreatic cancer, but people with a family history of the disease or certain risk factors, such as smoking or obesity, should talk to their doctor about getting tested.
- Ovarian cancer: There is no screening test for ovarian cancer, but women with a family history of the disease or certain risk factors, such as endometriosis or BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, should talk to their doctor about getting tested.
- Brain cancer: There is no screening test for brain cancer, but people with symptoms such as headaches, seizures, or vision changes should talk to their doctor.
If you are concerned about your risk of any of these cancers, please talk to your doctor. They can help you assess your risk and develop a plan for early detection.
Here are some tips for early detection of cancer:
- Be aware of your risk factors: Knowing your risk factors for cancer can help you be more vigilant about early detection. Some common risk factors for cancer include smoking, obesity, family history, and exposure to certain chemicals.
- Get regular checkups: Seeing your doctor for regular checkups is an important part of early detection. During your checkups, your doctor will ask you about your medical history and perform a physical exam. They may also order tests such as blood tests, imaging tests, and cancer screenings.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms of cancer: Early detection is most important when cancer is still in its early stages, when it is most treatable. Some common signs and symptoms of cancer include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, fever, night sweats, pain, changes in appetite, changes in bowel or bladder habits, a lump in the breast or other part of the body, changes in the skin, a persistent cough or hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, headache, seizures, vision changes, and numbness or tingling in the hands or feet. If you experience any of these symptoms, please see your doctor right away.
Cure for cancer: There is no one-size-fits-all cure for cancer. The best treatment for cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the age and overall health of the patient.
Some common cancer treatments include:
- Surgery: Surgery to remove the tumor or cancerous tissue is a common treatment for many types of cancer.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a type of drug therapy that kills cancer cells throughout the body.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy drugs target specific molecules that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells.
Cancer treatment can be very effective, and many people with cancer are cured. However, cancer treatment can also have side effects, which can vary depending on the type of treatment and the individual patient.
Prevention of cancer: There are a number of things that people can do to reduce their risk of developing cancer, including:
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Protecting yourself from the sun
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting regular cancer screenings
Early detection of cancer can save your life. By being aware of your risk factors, getting regular checkups, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of cancer, you can increase your chances of early detection and treatment.